SFU VS HGU, What should be the difference?
When we talk about EPON/GPON networks. One thing is sure that both are Passive Optical Network and since the power intake is zero, only end terminal required power. This is the reason why we call them Passive Optical Networks (PON). It has further sub categories depending upon the technology/standards.
PON offers economic benefits to implement and to reduce the fiber and copper equipment compare to point to point architectures. PON system is composed of below entities.
- Optical Line Terminal OLT
- Optical Network Unit ONU
- Optical Network Terminal ONT
- Optical Distribution Network: commonly known as ODN offers fiber routes for to connect all above network.
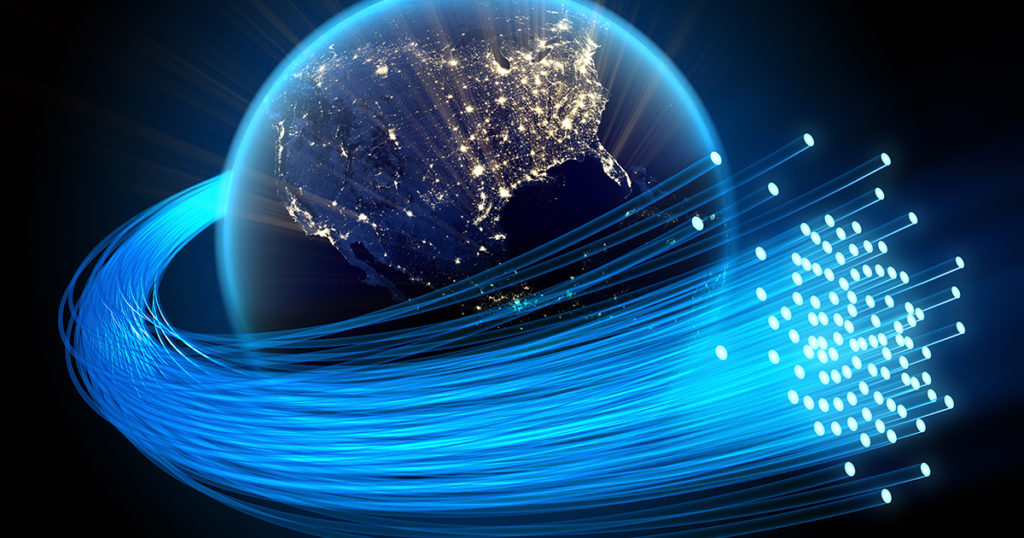
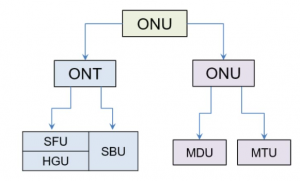
We will start with various types of ONUs and its further sub division into SFU (Single Family Unit) & HGU (House Gateway Unit).
ONU Optical Network Unit always deployed at customer premises. It works on IEEE standards as compared to ONTs which works on ITU-UT standards. When we speak of ONU port capacity, it always have same Uplink and downlink capacity which is 1.25 Gbps whereas for ONT the downlink/receive capacity is upto 2.5 Gbps and uplink/transmit up to 1.25 Gbps.
Downstream/Downlink data is transmitted over 1490 nm wavelength. All the downlink traffic is broadcasted to all the network elements on that side of the road, which is ONU in this case but only the intended ONU can receive the packet. Rest all the packets will be discarded.
Upstream/Uplink – Upstream/Uplink data is transmitted over 1310 nm wavelength as shown below but if CATV service is being utilized then same data will be transmitted over 1550 nm wavelength.
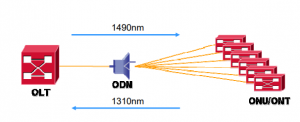
No matter in which scenario, ONU/ONT is being utilized. ONU/ONT will always have following interfaces.
- Ethernet (number of ports varies from type to type)
- Telephone which is called POT
- Wlan
- USB
- CATV RF Interface
ONU Types
There are 5 types of ONUs. All types of ONUs are based on application scenarios which can be data type, data + voice type, data + WiFi type, data + voice + WiFi type. We will discuss the first two types here.
- Single Family Unit SFU.
- Home Gateway Unit HGU.
- Single Business Unit SBU
- Multi Dwelling Unit MDU.
- Multi-Tenant Unit
Single Family Unit ONU (SFU)
In normal scenario SFU ONU uses VEIP. But in scenarios where VEIP is not being used or utilized, SFU ONU uses PPTP. OMCI management plane is supported by SFU ONU.
In OMCI data plane, all the packets can be transparently transmitted even without using any forwarding technique or MAC address learning. This feature is enabled due to one to one mapping of UNI port and GEM port, where GEM port is facing towards network backbone and UNI port is facing towards user end. OMCI does not support Wireless interfaces as the OMCI management data flow is not same as that of RG data flow.
The OAM of OMCI management plane supports OLT in configuring and managing Ethernet port of SFU ONU. SFU ONU allows multiple VLAN feature due to bridging mode. SFU ONU provides excellent service capabilities when it is coupled with a home gateway.
SFU is equipped with built-in IAD, the ONT provides users layer-II data and voice services as shown below. This scenario provides transparent transmission channel and requires simple service configuration and that is the reason, it applies to layer-II networking.
SFU ONU will always have minimum one and maximum four Ethernet interfaces and these ports can be used for Ethernet/IP services and in some scenarios VOIP services or CATV service.
Simply we can say that SFU ONU can be understood as Layer-II device, usually with no routing function. SFU ONU used in different FTTH scenarios as illustrated in below diagram.
Home Gateway Unit ONU (HGU)
The division between the OMCI management plane and the non-OMCI management plane which is the data plane is defined at Virtual Ethernet interface Point (VEIP).
The Non-OMCI Management domain can not only manage all services but it also manage functional modules under the VEIP. HGU ONU allows only one VEIP. MIB is uploaded as per the device type used. It can use VEIP or PTPP.
VEIP virtualizes the total interfaces of ONU. VEIP supports OLT and ONU in data blocking process. ONU supports VEIP to manage the services and their required configuration. And hence we can say that VEIP is the virtual WAN port in HGU.
PPPT which is basically physical path termination point. The whole data flow process is achieved by sending Vlan data directly to ONU where it is received at PPTP. In other words, PPTP is a LAN port concept.
Normally HGU ONU provides Ethernet/IP service/VOIP service and optional CATV service. HGU ONU support TR-069 remote management and EMS local and remote management.
HGU is a Layer-III device which makes it able to communicate on IP layer as well and this thing is achieved by routing function and compared with SFU, it has home gateway function as well.
When it is coupled with firewall or NAT router which then eradicates a need for a subscriber to install its own WiFi router to distribute internet in home or office, DHCP server, USB ports, storage or print server etc.
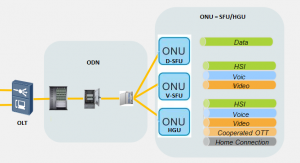
In above diagram, SFU ONT can be regarded as a pipe providing layer-II data and voice services. Whereas HGU/HGW ONT provide Layer-III services, which is center of the manageable home network and can be regarded as “tap” of the smart pipe.





